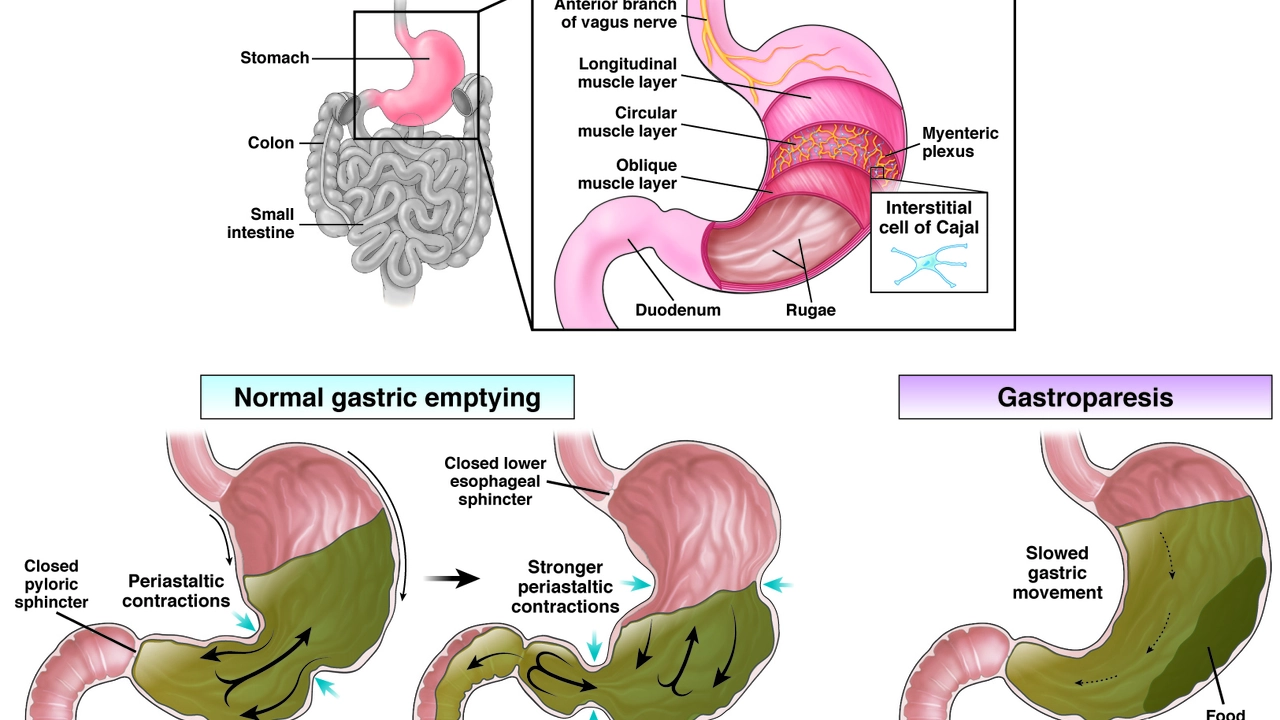
Understanding Diabetic Gastroparesis
Living with diabetes can be challenging, and when complications like gastroparesis arise, it can feel overwhelming. Gastroparesis can be described as a condition where your stomach takes too long to empty its contents, often due to damage to the vagus nerve which controls the movement of food through the digestive tract. This is a condition that is prevalent among diabetics, and it can cause symptoms ranging from mild discomfort to severe pain. This complication can make it difficult to manage blood sugar levels, leading to a vicious cycle of worsening symptoms and further health complications.
Managing Symptoms and Improving Digestion
One of the biggest challenges when dealing with diabetic gastroparesis is managing symptoms. These include nausea, vomiting, heartburn, bloating, and a feeling of fullness even after eating just a little food. One of the most effective ways to cope with these symptoms is through dietary adjustments. Eating smaller, more frequent meals can help, as well as avoiding high-fat and high-fiber foods which can slow digestion. Additionally, drinking plenty of water and exercising lightly after meals can aid digestion.
Effective Medication and Treatment Options
While there is currently no cure for diabetic gastroparesis, there are several medications and treatments available that can help manage symptoms and improve your quality of life. These include medications that stimulate stomach muscles, antibiotics to control bacteria, and medications to help control vomiting and nausea. In severe cases, feeding tubes or even a gastric pacemaker may be required. It's important to remember that everyone's body reacts differently to medications and treatments, so it may take some time and trial-and-error to find what works best for you.
Maintaining Blood Glucose Control
Maintaining blood glucose control is a key aspect of managing diabetic gastroparesis. This can be particularly challenging due to the unpredictable digestion times, which can cause blood sugar levels to fluctuate widely. Regular blood glucose monitoring is crucial, as well as adjusting insulin doses accordingly. It's also recommended that people with diabetic gastroparesis follow a consistent eating schedule, which can help to stabilize blood sugar levels throughout the day.
Emotional Well-being and Support
Coping with diabetic gastroparesis can be mentally and emotionally challenging. The constant worry about what to eat, when to eat, and how to manage symptoms can take a toll on your mental health. That's why it's important to seek emotional and psychological support. This can come in many forms, such as counseling, support groups, or even simply talking about your feelings with friends and family. Remember, you are not alone in this journey. There are many people out there facing similar challenges, and there are plenty of resources available to help you cope.

Raja M
July 16, 2023 AT 04:56Gastroparesis sucks, fight it or quit sugar!
Rob Flores
July 29, 2023 AT 01:39Oh, brilliant, another “how‑to” list-because we’ve never heard that before. If you think smaller meals magically fix nerve damage, you’re living in a utopia.
Shiv Kumar
August 10, 2023 AT 22:23One must consider the epistemological framework within which diabetic gastroparesis is presented; is it merely a physiological anomaly or a narrative device for the modern healthcare saga?
Ryan Spanier
August 23, 2023 AT 19:07Indeed, the importance of consistent monitoring cannot be overstated. Patients should collaborate closely with endocrine specialists, schedule regular appointments, and document meal‑insulin timing meticulously. This systematic approach fosters confidence and reduces the erratic glycemic swings associated with delayed gastric emptying.
Abhinav Moudgil
September 5, 2023 AT 18:38Managing diabetic gastroparesis is a marathon, not a sprint, and every step counts toward a better quality of life.
First, embrace the concept of “bite‑sized victories,” meaning you intentionally limit each portion to a size your stomach can comfortably handle.
Pair those mini‑meals with low‑glycemic carbohydrates such as quinoa, oats, or berries, which slow the glucose surge and give your pancreas a breathing room.
Hydration plays a starring role; sip clear fluids between bites rather than gulping a soda that can bloat your gut.
Light movement, like a gentle walk for ten minutes after eating, stimulates peristalsis without overtaxing your cardiovascular system.
Consider incorporating ginger or peppermint teas, both of which have been anecdotally reported to soothe nausea and accelerate gastric transit.
Medication adherence is non‑negotiable-prokinetics, anti‑emetics, and targeted antibiotics each address a distinct facet of the disorder.
Keep a detailed log of which drugs alleviate your symptoms and which seem to wobble the needle in the wrong direction.
When insulin dosing, remember that delayed absorption may require a lower pre‑meal bolus and a possible correction dose later in the evening.
Frequent glucose checks, ideally every two to three hours, will illuminate patterns that static measurements miss.
If you encounter persistent vomiting or severe weight loss, discuss advanced interventions such as a gastric electrical stimulator with your gastroenterologist.
Support networks, whether online forums or local meet‑ups, provide emotional scaffolding that mitigates the isolation many patients feel.
Sharing recipes tailored for gastroparesis-think smooth soups, creamy purees, and nutrient‑dense smoothies-can spark creativity in the kitchen.
Remember, mental health is intertwined with physical health; mindfulness practices can dull the stress response that aggravates gastrointestinal motility.
Celebrate each small triumph, whether it’s a day without nausea or a stable blood‑sugar reading, because those moments accumulate into lasting resilience.
Ultimately, a personalized, multidisciplinary strategy transforms a daunting diagnosis into a manageable chapter of your life.
Miah O'Malley
September 18, 2023 AT 18:08The interplay between mind and gut is profound; nurturing emotional well‑being can literally smooth the digestive rhythm, turning frustration into acceptance and fostering a gentler relationship with food.
Bradley Allan
October 1, 2023 AT 14:52!!!THIS IS WHAT HAPPENS WHEN MEDICAL RESEARCH FAILS TO KEEP UP!!!
EVERY DAY IS A BATTLE, EVERY MEAL A WARZONE!!!
AND YET WE STAND, WE STRUGGLE, WE REFUSE TO BE DEFEATED!!!
Kyle Garrity
October 14, 2023 AT 11:36Hey, I get how exhausting it can feel to constantly juggle blood sugar spikes and the gnawing emptiness after meals. Finding that sweet spot with portion sizes takes trial and error, but keep tracking what works; it’ll pay off in steadier numbers and less nausea.
brandon lee
October 27, 2023 AT 08:20Just take it easy, stick to small meals and move a bit after eating, it usually helps.
Joshua Pisueña
November 9, 2023 AT 04:03Sounds good just keep it simple stay consistent with meals and meds
Ralph Barcelos de Azevedo
November 22, 2023 AT 00:47Honestly, most of the advice out there feels like recycled boilerplate; unless you have a specialist who actually listens, you’re just spinning wheels on generic recommendations.
Peter Rupar
December 4, 2023 AT 21:31Bruh u cant just blame the doc they prob didnt even read the smaill print on the med guide lol its on u to figure it out
Nikita Shue
December 17, 2023 AT 18:15Yo, smash those mini‑meals like a champ, stay hydrated, and keep that insulin on point – you got this, no excuses!
Heather McCormick
December 30, 2023 AT 14:59Oh wow, another motivational pep talk-because what you really need is a louder voice telling you to “stay positive” while your stomach throws a tantrum.